Soil Characteristics Impacting Performance
- Soil type affects load-bearing capacity.
- Moisture content influences stability.
- Site preparation ensures a solid base.
Ever wondered how the foundations of your building stay stable and resilient? The answer lies in understanding the vital role of structural concrete slabs. These slabs not only support loads but also ensure the safety and longevity of your construction projects, making it essential to grasp their characteristics and applications.
Understanding the fundamental properties and environmental aspects that influence concrete slab performance.
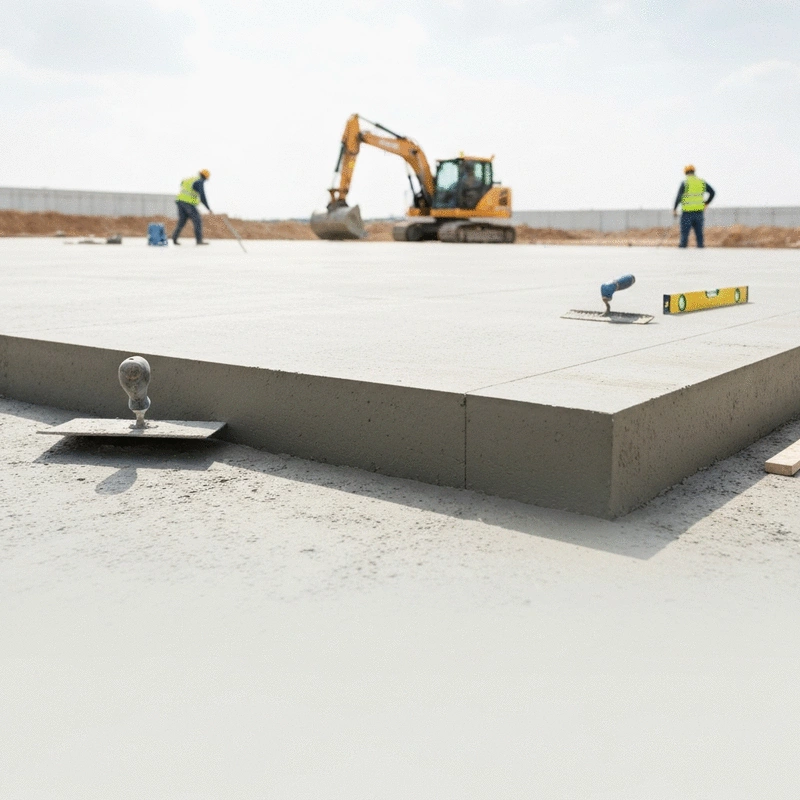
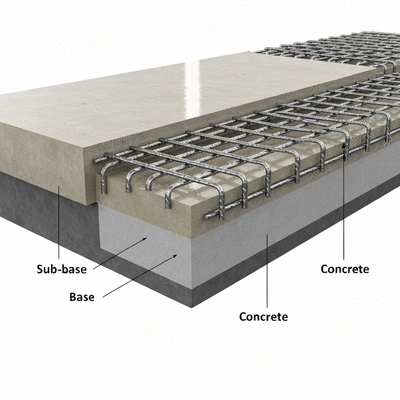
When we talk about structural concrete slabs, we're referring to flat horizontal surfaces constructed from concrete, designed to support loads within buildings and other structures. These slabs are crucial elements in construction, providing the foundation for floors, ceilings, and roofs. Understanding their definition and importance can significantly improve project outcomes, which is what we at Concrete Slab Innovations aim to achieve.
A structural concrete slab is essentially a thick, solid layer of concrete that is both strong and durable. Typically, these slabs are designed to distribute loads over a larger area, ensuring stability and support. The thickness and reinforcement of these slabs depend on various factors, including the intended use and the loads they will bear. Have you ever considered the various types of slabs, such as one-way and two-way slabs, and how they function differently?
Each type has its benefits, so selecting the right slab for your project is key to ensuring structural integrity.
Concrete slabs play a vital role in the overall structural system of a building. They provide essential support, contributing to the stability and longevity of the structure. Furthermore, high-load engineering solutions often utilize concrete slabs, allowing for the efficient distribution of forces during various load conditions.
In short, understanding the role of concrete slabs ensures that every project is built on a solid foundation—literally and figuratively! By focusing on innovative solutions, we can improve efficiency and safety during construction.
The performance of concrete slabs is often influenced by the soil beneath them. Understanding soil characteristics is crucial because they determine how the slab will behave under load. For example, clay soils tend to expand and contract with moisture changes, which can lead to cracking if not properly managed. For more information on how soil characteristics affect slab performance, you can consult resources such as the NRCS Design Guide for Slabs-on-Ground.
A thorough soil analysis before construction can save time and costs down the line.
Understanding load transfer mechanisms is vital for the design and performance of concrete slabs. Load transfer occurs through bending and shear forces, ensuring that the loads applied to the slab are adequately supported and distributed. This is where reinforcement becomes essential, providing the necessary strength to handle various load conditions. For a comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms, the Wisconsin Department of Transportation's Bridge Manual, Chapter 18 provides excellent insights into structural concrete design.
By understanding these mechanisms, we can create more effective designs that enhance performance and safety.
Reinforcement in concrete slabs—typically through steel bars or mesh—provides the necessary tensile strength to resist cracking and failure under load. The demand for reinforcement is influenced by the type of slab, expected loads, and environmental conditions. At Concrete Slab Innovations, we emphasize the importance of selecting the right reinforcement methods for each project.
By addressing reinforcement demand early in the design phase, significant structural issues can be avoided later.
Load-bearing capacity refers to the maximum weight a concrete slab can support without failure. It's crucial to calculate this capacity during the design phase to prevent structural collapse. Factors such as slab thickness, reinforcement type, and soil conditions all contribute to load-bearing capacity.
Understanding and designing for load-bearing capacity ensures that your project stands the test of time!
When selecting the type of structural concrete slab for your project, consider not only the load requirements but also the environmental conditions of the site. For instance, if you are working in an area with expansive clay soil, a two-way slab may provide better load distribution and reduce the risk of cracking compared to a one-way slab. Always consult with an engineer to tailor your approach to the specific needs of your project!
A structural concrete slab is a thick, solid layer of concrete designed to support loads within buildings, acting as a foundation for floors, ceilings, and roofs, ensuring stability and durability.
The main types are one-way slabs (support loads in one direction), two-way slabs (distribute loads in multiple directions for larger spans), and flat slabs (rely on column support without beams).
Soil type (e.g., sand, clay) and moisture content significantly impact a slab's load-bearing capacity and stability. Proper site preparation is crucial to provide a solid base and prevent issues like cracking due to soil expansion or contraction.
Reinforcement, typically steel bars or mesh, provides tensile strength to concrete slabs, preventing cracking and failure under various loads. Correct placement and adherence to building codes are essential for maximizing its effectiveness and ensuring safety.
The load-bearing capacity depends on factors such as slab thickness, the type and amount of reinforcement used, and the underlying soil conditions. Engineers calculate this capacity with safety factors to account for unexpected loads.
Eco-friendly strategies include using low-carbon cement alternatives, incorporating supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag, utilizing recycled aggregates, and adopting carbon capture technologies. These measures reduce the embodied carbon and overall environmental impact.
As we move towards more sustainable building practices, the environmental impact of construction materials has come to the forefront. At Concrete Slab Innovations, we believe that incorporating environmentally friendly approaches in concrete slab design is essential. By focusing on reducing the embodied carbon in concrete, we can significantly enhance the sustainability of our projects.
Incorporating eco-friendly strategies can lead not only to a decreased carbon footprint but also to improved project efficiency. Here are some effective methods to consider:
By embracing these strategies, we can contribute to a cleaner environment while still achieving high-quality results. Isn't it exciting to think about how we can align our goals with sustainability?
Reducing embodied carbon in concrete involves careful planning and material selection. At Concrete Slab Innovations, we prioritize strategies that not only minimize emissions but also maintain the integrity and performance of our slabs. Here are key strategies to keep in mind:
These approaches help lower the overall carbon emissions associated with concrete production. Adopting them not only benefits the environment but also enhances the marketability of your projects!
Choosing the right materials is crucial for creating sustainable slabs. The selection process can make a substantial difference in the overall performance and environmental impact. Consider these eco-friendly materials:
By opting for these materials, we not only improve the sustainability of our construction practices but also ensure that our slabs are durable and reliable.
The durability of concrete is essential for longevity and performance. At Concrete Slab Innovations, we emphasize the importance of designing slabs that can withstand environmental stresses. Key considerations include:
By focusing on these aspects, we can ensure that our concrete slabs not only meet current needs but also stand the test of time.
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:


 Have you ever considered how choosing the right formwork can significantly impact your project's eff
Have you ever considered how choosing the right formwork can significantly impact your project's eff
 Consider this: the effective use of aluminum formwork can significantly streamline your construction
Consider this: the effective use of aluminum formwork can significantly streamline your construction
 What if the key to revolutionizing your construction project lies in the materials you choose? Alumi
What if the key to revolutionizing your construction project lies in the materials you choose? Alumi
 As high-rise construction evolves, aluminum formwork is emerging as a game-changer for contractors a
As high-rise construction evolves, aluminum formwork is emerging as a game-changer for contractors a